Embark on an in-depth exploration of quadratic functions standard form assignment, where we unravel the intricacies of these equations and their applications in the real world. Delve into their properties, graphing techniques, and solution methods, gaining a comprehensive understanding that will empower you to conquer any quadratic challenge.
Quadratic functions, represented in their standard form, provide a systematic approach to understanding their behavior. We will examine the vertex, axis of symmetry, and range, unlocking insights into their graphical representations. Moreover, we will explore the art of graphing these functions, establishing a connection between their standard form and the shape of their parabolas.
Quadratic Functions Standard Form: Quadratic Functions Standard Form Assignment
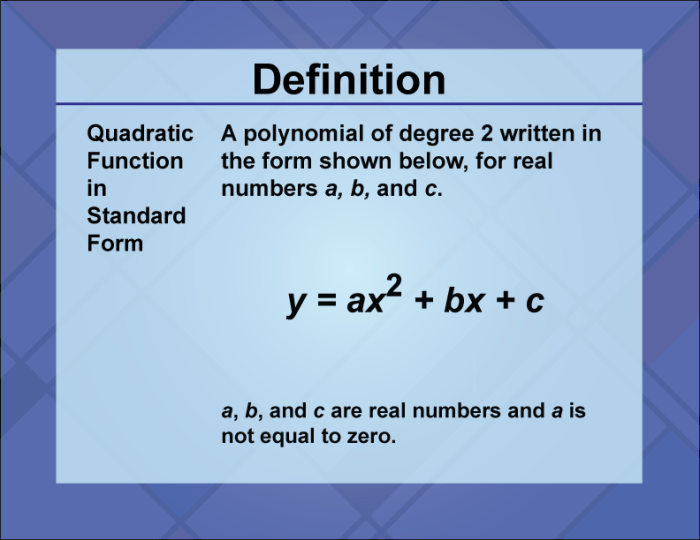
Quadratic functions are a type of polynomial function that has a squared term. They are represented in the standard form as:
f(x) = ax² + bx + c
where a, b, and care constants and a≠ 0.
Examples of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form, Quadratic functions standard form assignment
- f(x) = x²- 5x + 6
- f(x) = 2x² + 3x- 1
- f(x) =-x² + 4x + 2
Properties of Quadratic Functions
Quadratic functions have several important properties:
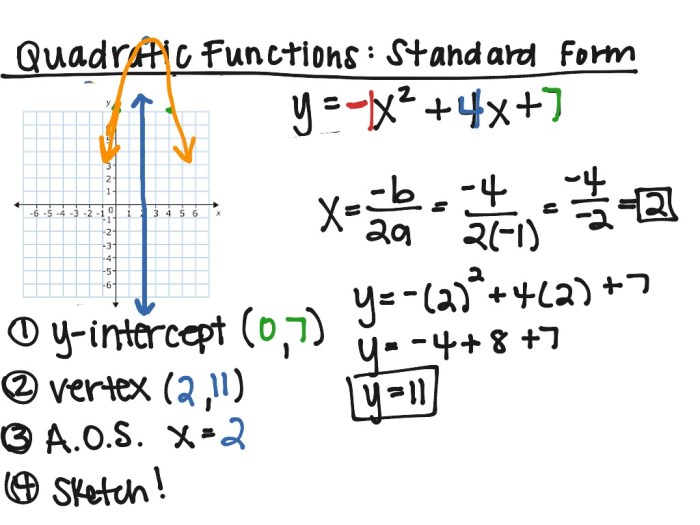
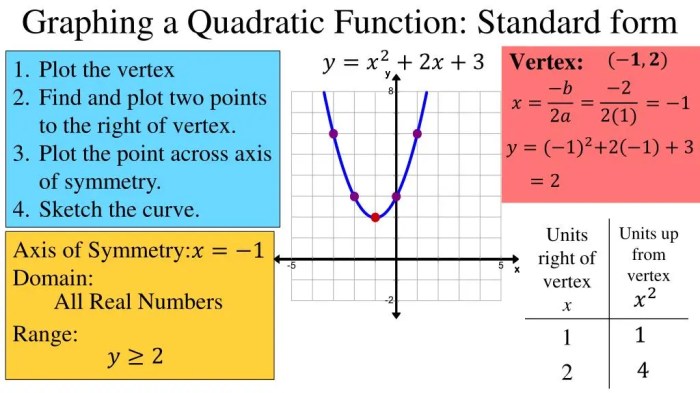
- Vertex:The vertex of a parabola is the point where the parabola changes direction. The vertex of a quadratic function in standard form is given by the coordinates:
(h, k) = (-b/2a, f(-b/2a))
- Axis of Symmetry:The axis of symmetry of a parabola is a vertical line that passes through the vertex. The axis of symmetry of a quadratic function in standard form is given by the equation:
x =-b/2a
- Range:The range of a quadratic function is the set of all possible output values. The range of a quadratic function in standard form is either [-∞, ∞)or (-∞, ∞).
Graphing Quadratic Functions
To graph a quadratic function using its standard form, follow these steps:
- Find the vertex of the parabola.
- Draw the axis of symmetry.
- Plot the vertex and at least one other point on the parabola.
- Connect the points to form the parabola.
The shape of the parabola depends on the value of a. If a> 0, the parabola opens upward. If a< 0, the parabola opens downward.
Solving Quadratic Equations
There are several methods for solving quadratic equations, including:
- Factoring:If the quadratic equation can be factored, it can be solved by setting each factor equal to zero and solving for x.
- Completing the Square:This method involves completing the square of the quadratic expression and then taking the square root of both sides of the equation.
- Quadratic Formula:The quadratic formula is a general formula that can be used to solve any quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is:
x = (-b ± √(b²- 4ac)) / 2a
Applications of Quadratic Functions
Quadratic functions have many real-world applications, including:
- Projectile Motion:The trajectory of a projectile can be modeled by a quadratic function.
- Optimization Problems:Quadratic functions can be used to solve optimization problems, such as finding the maximum or minimum value of a function.
Helpful Answers
What is the standard form of a quadratic function?
The standard form of a quadratic function is ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0.
How do I find the vertex of a quadratic function?
The vertex of a quadratic function in standard form is located at (-b/2a, f(-b/2a)).
What is the axis of symmetry of a quadratic function?
The axis of symmetry of a quadratic function in standard form is x = -b/2a.