Neuron anatomy and physiology review sheet exercise 13 – Embark on a journey into the intricacies of neuron anatomy and physiology through Review Sheet Exercise 13, a comprehensive resource designed to illuminate the fundamental concepts that govern neuronal function. This exercise delves into the structural components and physiological processes that enable neurons to communicate, process information, and orchestrate the symphony of life.
Prepare to unravel the mysteries of the neuron, exploring its intricate anatomy and the dynamic processes that govern its function. Discover the role of the cell body, dendrites, and axon in shaping neuronal communication. Delve into the mechanisms of action potential generation and propagation, unraveling the secrets of neuronal excitability.
Uncover the diverse array of neurotransmitters and their pivotal role in synaptic transmission.
Neuron Anatomy and Physiology: Neuron Anatomy And Physiology Review Sheet Exercise 13
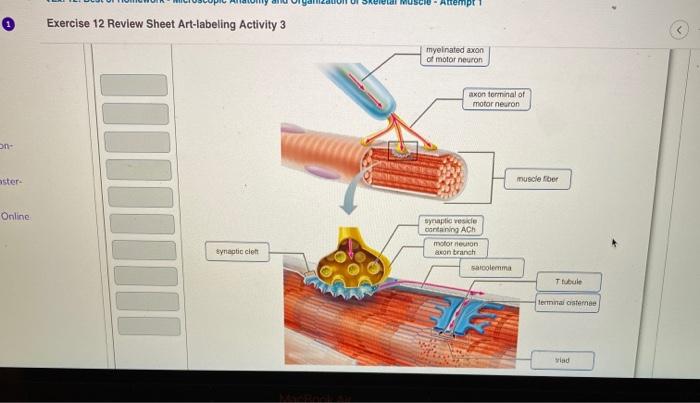
Neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, play a critical role in transmitting information throughout the body. Understanding their anatomy and physiology is essential for comprehending the functioning of the nervous system.
Neuron Anatomy
A neuron consists of several key components:
- Cell body (soma):Contains the nucleus and organelles, and serves as the metabolic center of the neuron.
- Dendrites:Short, branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons.
- Axon:A long, slender projection that transmits signals away from the cell body.
- Myelin sheath:A lipid-rich layer that surrounds the axon, insulating it and increasing the speed of signal transmission.
Neuron Physiology
Neurons communicate by generating and transmitting electrical signals called action potentials:
- Action potential generation:Occurs when the membrane potential reaches a threshold, causing a rapid influx of sodium ions into the neuron.
- Action potential propagation:The depolarization wave travels down the axon, thanks to ion channels that allow sodium and potassium ions to flow in and out.
- Neurotransmitters:Chemical messengers released at the axon terminals that bind to receptors on other neurons, transmitting the signal.
Review Sheet Exercise 13
Multiple Choice Questions:
- Which part of the neuron receives signals from other neurons?
- What is the role of the myelin sheath?
- Which ion channel is responsible for the initial depolarization of the neuron?
Short Answer Questions:
- Describe the process of action potential propagation.
- Explain the role of neurotransmitters in neuron communication.
Essay Question:
- Discuss the importance of neuron anatomy and physiology in understanding the functioning of the nervous system.
Additional Resources, Neuron anatomy and physiology review sheet exercise 13
- Structure of a Neuron | Khan Academy
- Ion Channels in Neuronal Excitability | Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience
Helpful Answers
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
The myelin sheath acts as an insulating layer around the axon, increasing the speed and efficiency of electrical signal transmission.
How are action potentials generated?
Action potentials are generated through a sequence of ion channel openings and closings, leading to a rapid change in membrane potential.
What are the different types of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are classified into various categories based on their chemical structure and function, including excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters.