Which of the following is true about impervious building materials? This question delves into the realm of construction, where the selection of building materials plays a crucial role in shaping the functionality, durability, and environmental impact of structures. Impervious building materials, with their unique properties and applications, offer both advantages and disadvantages, making their understanding essential for informed decision-making in the construction industry.
Impervious building materials, as the name suggests, are materials that do not allow the passage of water or other liquids. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications where water resistance is paramount, such as roofing, siding, and flooring. However, their impervious nature also raises concerns about their environmental impact, particularly regarding stormwater runoff and urban heat island effects.
1. Impervious Building Materials
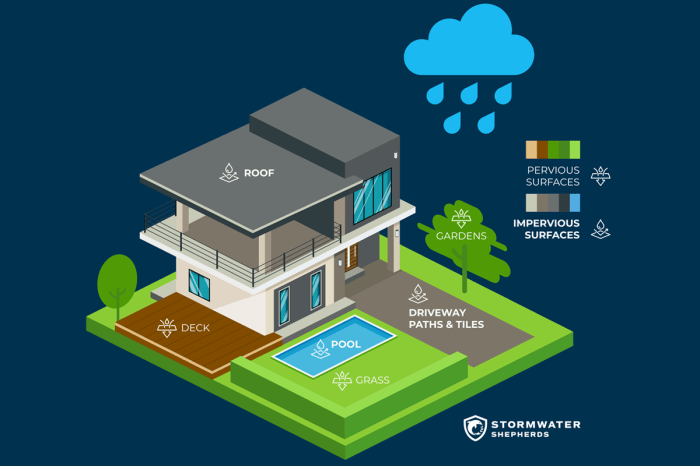
Impervious building materials are those that do not allow water to penetrate or pass through them. They are typically used in construction to prevent water damage and to create a waterproof barrier.
Examples of impervious building materials include:
- Asphalt
- Concrete
- Metal
- Plastic
- Rubber
There are several advantages to using impervious building materials:
- They can help to prevent water damage to buildings and structures.
- They can create a waterproof barrier that can protect against moisture and humidity.
- They can be used to create a variety of architectural features, such as roofs, walls, and floors.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using impervious building materials:
- They can be expensive to install and maintain.
- They can contribute to stormwater runoff and flooding.
- They can create a heat island effect in urban areas.
2. Types of Impervious Building Materials
| Material Type | Properties | Applications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asphalt | Waterproof, durable, flexible | Roofs, pavements, driveways | Asphalt shingles, asphalt paving |
| Concrete | Strong, durable, fire-resistant | Foundations, walls, floors | Concrete blocks, concrete slabs |
| Metal | Waterproof, durable, corrosion-resistant | Roofs, siding, gutters | Metal roofing, metal siding |
| Plastic | Waterproof, lightweight, flexible | Windows, doors, siding | Vinyl siding, PVC pipes |
3. Applications of Impervious Building Materials
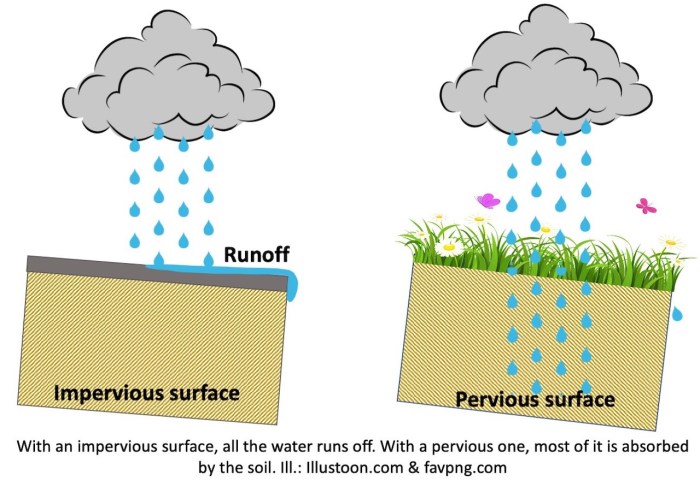
Impervious building materials are used in a wide variety of construction projects, including:
- Residential buildings
- Commercial buildings
- Industrial buildings
- Infrastructure projects
In residential buildings, impervious building materials are used to create roofs, walls, and floors. In commercial buildings, they are used to create roofs, walls, floors, and parking garages. In industrial buildings, they are used to create roofs, walls, floors, and storage tanks.
In infrastructure projects, they are used to create roads, bridges, and tunnels.
One example of a successful application of impervious building materials is the use of asphalt shingles to create a waterproof roof on a residential home. Another example is the use of concrete to create a durable foundation for a commercial building.
4. Environmental Impact of Impervious Building Materials

The use of impervious building materials can have a negative impact on the environment.
One of the main concerns is that impervious building materials can contribute to stormwater runoff and flooding. When rain falls on impervious surfaces, it cannot soak into the ground. Instead, it runs off into storm drains and can cause flooding.
Flooding can damage property and infrastructure, and it can also lead to water pollution.
Another concern is that impervious building materials can create a heat island effect in urban areas. Heat island effects occur when the temperature in an urban area is significantly higher than the temperature in the surrounding rural areas. This is because impervious building materials absorb and release heat more quickly than natural surfaces, such as trees and grass.
Heat island effects can lead to increased air pollution, heat-related illnesses, and energy consumption.
5. Sustainability Considerations for Impervious Building Materials: Which Of The Following Is True About Impervious Building Materials
There are a number of sustainable alternatives to impervious building materials.
One option is to use pervious pavements. Pervious pavements are made from materials that allow water to infiltrate into the ground. This can help to reduce stormwater runoff and flooding, and it can also help to cool urban areas.
Another option is to use green roofs. Green roofs are roofs that are covered with vegetation. Vegetation can help to absorb rainwater, reduce stormwater runoff, and cool urban areas.
By using sustainable alternatives to impervious building materials, we can help to reduce the environmental impact of construction.
FAQ Resource
What are the advantages of using impervious building materials?
Impervious building materials offer several advantages, including excellent water resistance, durability, and low maintenance requirements. They are also resistant to rot, decay, and insect damage, making them ideal for long-lasting applications.
What are the disadvantages of using impervious building materials?
Impervious building materials can contribute to stormwater runoff and urban heat island effects. They can also be more expensive than pervious materials and may require specialized installation techniques.
What are some sustainable alternatives to impervious building materials?
Sustainable alternatives to impervious building materials include pervious pavements, green roofs, and rain gardens. These alternatives allow water to infiltrate the ground, reducing runoff and mitigating urban heat island effects.